
For example, the combination of IP address 10.0.0.1/24 on the ether1 interface and IP address 10.0.0.132/24 on the ether2 interface is invalid, because both addresses belong to the same network 10.0.0.0/24. Two IP addresses from the same network assigned to routers different interfaces are not valid unless VRF is used. For example, if the physical interface you assigned the address to, is included in a bridge, the actual interface will show that bridge
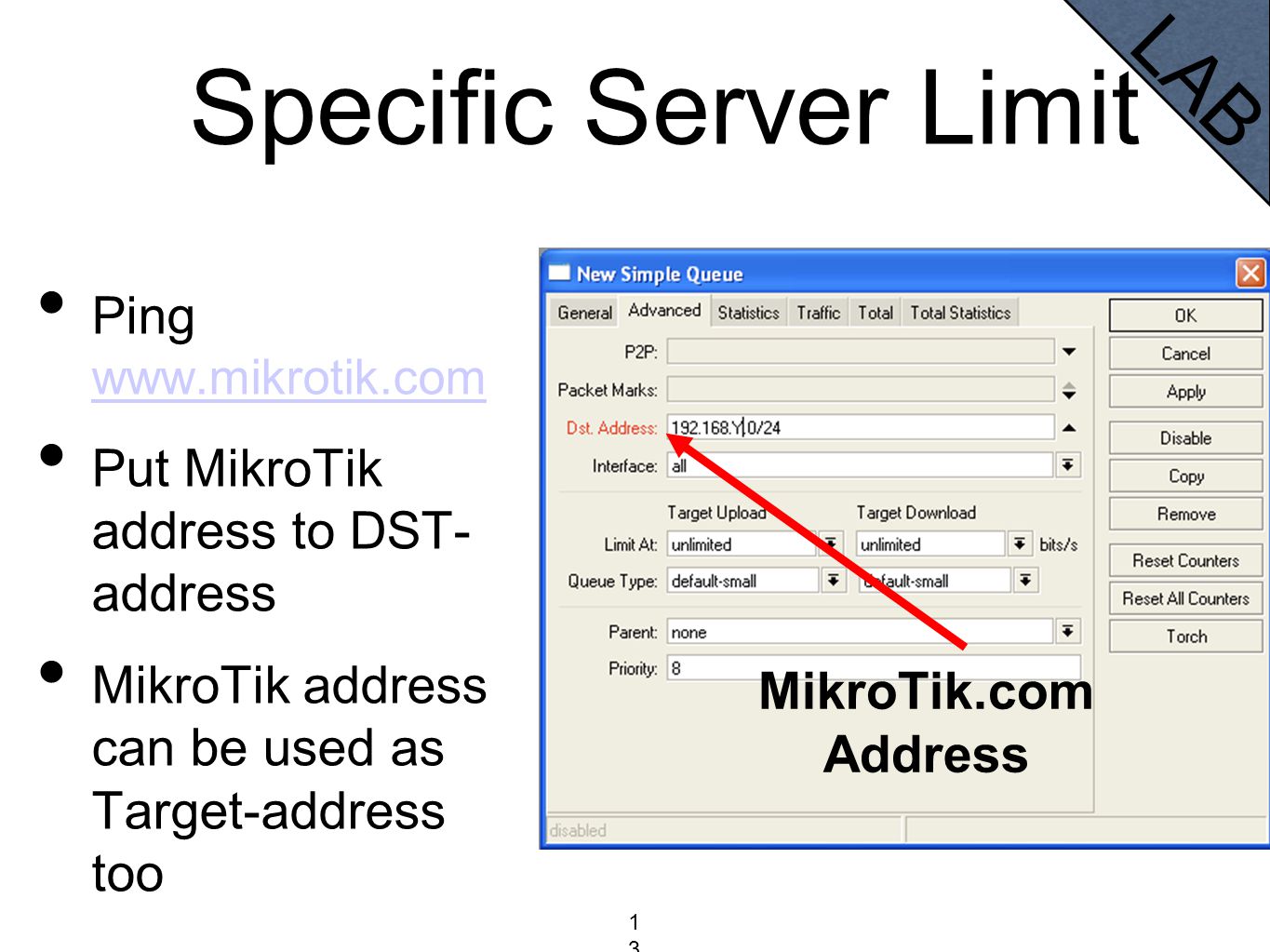
Name of the actual interface the logical one is bound to. Starting from v5RC6 this parameter is configurable only for addresses with /32 netmask (point to point links) For point-to-point links it should be the address of the remote end. Interface name the IP address is assigned toĭelimits network address part of the IP address from the host part Starting from v5RC6 this parameter is removed Roadcasting IP address, calculated by default from an IP address and a network mask. Dynamic - automatically assigned to the interface by DHCP or an estabilished PPP connectionsīroadcast ( IP Default: 255.255.255.255).Static - manually assigned to the interface by a user.MikroTik RouterOS has following types of addresses: You can use /ip address print detail to see to which interface the address belongs to. Putting an IP address to a physical interface included in a bridge would mean actually putting it on the bridge interface itself. In case of bridging or PPPoE connection, the physical interface may bot have any address assigned, yet be perfectly usable.
It is possible to add multiple IP addresses to an interface or to leave the interface without any addresses assigned to it. The network prefix and the broadcast address are calculated automatically. In most cases, it is enough to specify the address, the netmask, and the interface arguments.

It's also possible to specify IP address followed by slash "/" and the amount of bits that form the network address.

The network address value is calculated by binary AND operation from network mask and IP address values. For proper addressing the router also needs the network mask value, id est which bits of the complete IP address refer to the address of the host, and which - to the address of the network. Typical (IPv4) address consists of four octets. IP addresses serve for a general host identification purposes in IP networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
